Elements of the Halogen Family __________ One Electron to Become Halide Ions.
Place halide ions - chloride, bromide, iodide
In this lesson, we are going to identify halide ions. chloride, bromide, iodide. We report what compounds are used to place halide ions and what are the observations we can meet after halide ions testing. Some halide ions compounds dissolve in water and some form precipitates. According to the concrete land and halide ion, nosotros choose different methods and reagents to test halide ion.
What is a halide ion?
Halide ion the anion of halogen atom. The charge of halide ion is -ane. F-, Cl-, Br-, I- are the halide ions. These halide ions take some simialar properties and unlike properties.
All of those halides are in -ane oxidation country. Also these halides can exist presence as solid state or solution country. Some of these halide compounds are precipitates. Co-ordinate to the land, we have to change the experimental method to place the ion.
Identify halide ions in solution state
Here, we are going to discuss about iii different methods to identify halide ions which exist such equally NaCl(aq) , KI(aq) .
Place chloride ion in solution state
- Add together lead(2) acetate ( Pb(CH3COO)two ) or lead(ii) nitrate ( Lead(NO3)ii ). It will give white precipitate of atomic number 82(2) chloride (PbCl2). Besides this precipitate will melt in hot water and when it cools again, it will precipitate once again.
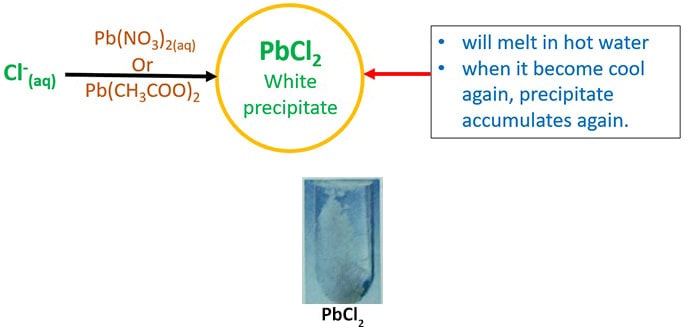
- Add first dilute HNO3 and and then AgNO3(aq).
It will requite AgCl white precipitate which solve in dilute NHthree.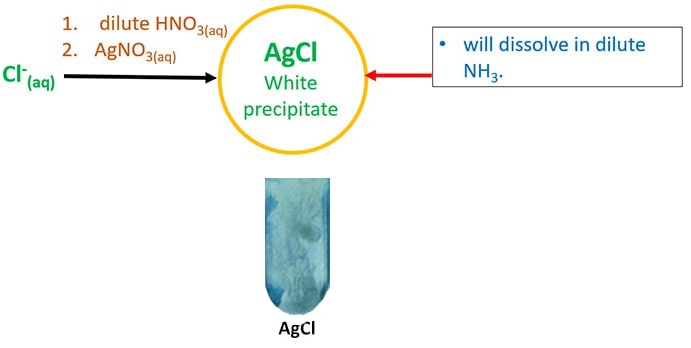
- Add together CHCl3 or CClfour and joggle the mixture.
Information technology will give colourless layer.
Place bromide ion in solution country
- Add lead(ii) acetate ( Pb(CH3COO)2 ) or lead(ii) nitrate ( Atomic number 82(NOiii)2 ). Information technology volition requite white(foam) precipitate of lead(ii) bromide(PbBr2). Too this precipitate will melt in hot water and when it cools over again, it volition precipitate over again.
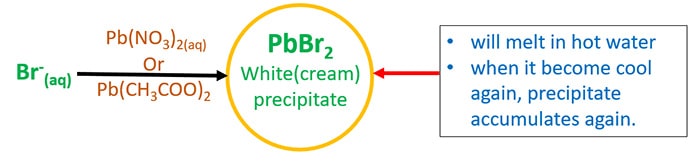
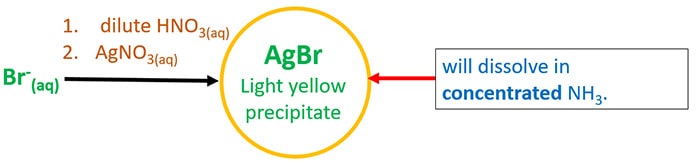
- Add first dilute HNO3 and then AgNO3(aq).
It will give AgBr lite yellow precipitate which solve in conc. NHthree.
- Add together CHCl3 or CCliv and joggle the mixture.
Information technology will requite dark-brown/orange globule.
Identify iodide ion in solution state
- Add lead(ii) acetate ( Pb(CH3COO)2 ) or lead(ii) nitrate ( Pb(NO3)ii ). Information technology will give yellow precipitate of lead(ii) bromide(PbI2). This precipitate will melt when it's humid. And then cool the solution again, it will deposit as a gold yellow powder.
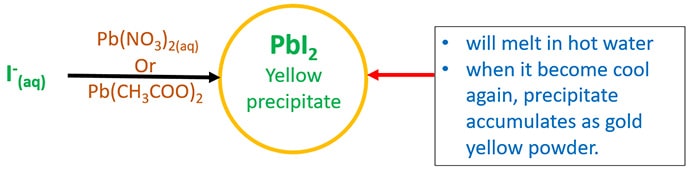
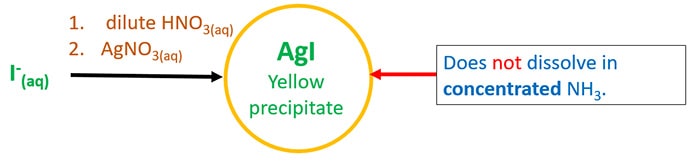
- Add commencement dilute HNO3 and so AgNO3(aq).
It volition requite AgI xanthous precipitate which doesn't solve NH3.
- Add together CHClthree or CCl4 and joggle the mixture.
Information technology will give purple globule.

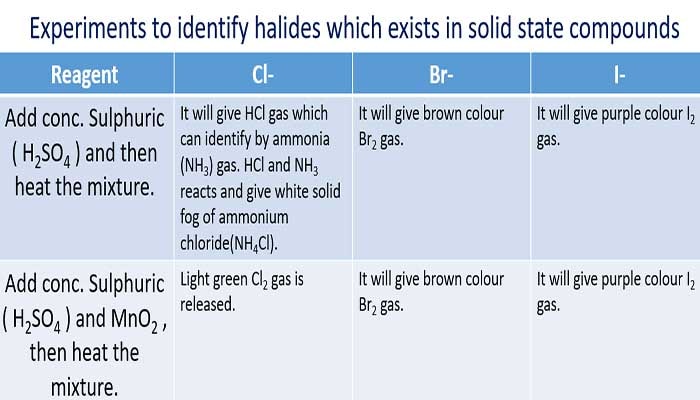
Identify halide ions in solid state
Here, we are going to discuss nearly 2 different methods to identify halides which exist as solids such as NaCl(s), KI(s)
Identify chloride ion in solid state compounds
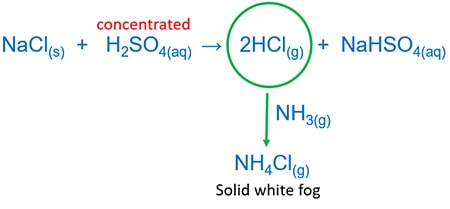
Concentrated sulphuric acid and solid chloride then rut the mixture.
It will give NaHSO4 and HCl gas. HCl can exist identified by ammonia (NH3) gas. HCl and NH3 reacts and give white solid fog of ammonium chloride(NHivCl).
Concentrated sulphuric acid, MnOii and solid chloride compound , then heat the mixture.
Manganese dioxide(MnOtwo) is a oxidizing agent which oxidizes chloride ions into chlorine gas. Low-cal xanthous green color Cl2 gas is released in the reaction.Cliiis a toxic gas.

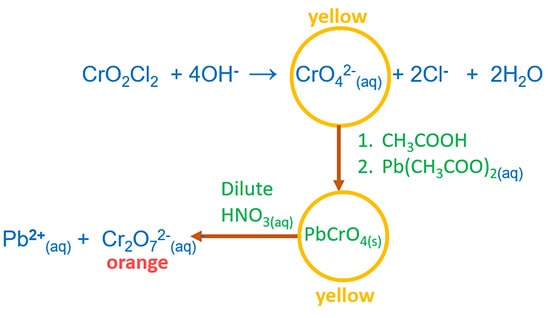
Chromyl Chloride Test to identify chloride ion
Add together K2Cr2O7, full-bodied H2So4 to solid chloride. Then heat the mixture. A blood-red colour vapour CrO2Cl2 is formed.
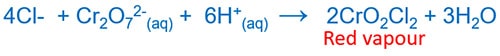
Add NaOH. CrOtwoCl2 and OH- react to requite yellow solution CrO4 2-. Then add CHiiiCOOH and Atomic number 82(CH3COO)two. A yellow colour PbCrO4 precipitated is formed. PbCrOiv(s) solve in dilute HNOthree.
Identify bromide ion - solid state compounds
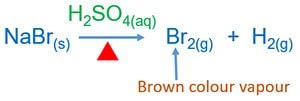
Concentrated sulphuric acid and solid bromide compounds so supply heat to the mixture
Information technology will give brownish colour Brtwo gas. Hii gas also is given.
NaCl(south) gives HBr with concentrated H3PO4.
When hot concentrated HiiiPO4 acid is added to solid NaCl, HBr vapour is formed.
Concentrated sulphuric, MnO2 with solid bromide compounds, then estrus the mixture.
Information technology will give dark-brown color Brtwo gas. MnO2 is reduced to Mn2+ ions.
Identify iodide ion in solid state compounds
Concentrated sulphuric acid and solid iodide chemical compound, then heat the mixture.
Iodide ion is oxidized and it volition give imperial colour I2 gas. Also hydrogen gas is given.
Full-bodied sulphuric acid, MnO2 and solid iodide compound and then estrus the mixture.
Information technology will give majestic colour I2 gas.
KI and HiiiPO4
HI is formed. H3PO4 is not a oxidizing acid.

KI(s), 10002Cr2Oseven and HtwoSOiv(aq) reaction
Purple colour I2 is given. Also Cr3+ is formed. But cherry CrO2Clii vapour is not given.

Iodide ion and Cu2+ or Fethree+ reaction
I2 is released. I2 can exist identified past farina.
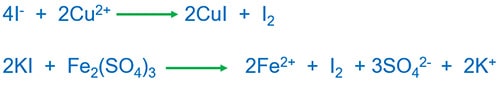
Halide ions of brine metals
All alkali metal halide compounds are high melting crystalline solids. All alkali metallic halide compounds are soluble in water exception of LiF. LiF is insoluble in water due to its loftier lattice energy because of small cation and small anion size. Other halide ions of lithium are soluble in ethanol, acetone, ethyl acetate. LiCl is soluble in pyridine. CsI has also low solubility due to smaller hydration energy of its two ions.
Halide ions of brine earth metals
Being covalent BeCl2 is soluble in organic solvents. MgCltwo, MgBrii are soluble in organic solvents. BeCl2 has low melting betoken and BaCltwo has higher melting points. Fluorides of alkali earth metals are sparingly soluble in water. The solubility increases slightly with increase of cation size. All brine earth metals are ionic and soluble in water except BeClii.
Colours of halide compounds
Some halide compounds have colours. Below all compounds are precipitates.
- PbClii(southward) : white
- PbBrtwo(s) : white cream
- PbI2(s) : yellow
- AgCltwo(southward) : white
- AgBrii(due south) : light yellow
- PbI2(s) : yellow
Hydrogen halides
Hydrogen halides are the near useful compounds of halogens. HCl, HBr, HI are strong acids and HF is a weak acid. All of the hydrogen halides are very soluble in water. HCl, HBr, Hi are well-nigh completely dissociated in dilute solutions.
Preparing hydrogen halides
Heating a table salt containing the halide ion with a nonvolatile acid is the usual way in which HF, HCl, and HBr are obtained in laboratory experiments.
Preparing HCl, HBr and Hello

But this method cannot use to prepare Hi because Howdy is non relatively stable than other hydrogen halides.
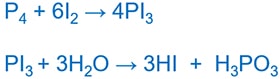
Preparing Hi
prepare a compound containing iodine,then acquit out a hydrolysis reaction.
Questions of halide ions
How do you place sodium chloride and sodium bromide solution?
There are two colourless aqueous solutions without labels. But students have been informed that those two solutions are sodium chloride and sodium bromide. You are advised that. Propose a method to place these 2 solutions.
Sodium ion is common in ii solutions. And then we have to do the testing for chloride ions and bromide ion.
Showtime add dilute nitric acid and and then pb nitrate solution. You can notice that a white precipitate and lite yellow precipitate grade in two solutions. White precipitate is lead chloride. Now nosotros can place 2 solutions from comparison colours of two precipitates.
How do you identify sodium nitrite and sodium bromide?
Both sodium bromide and sodium nitrite are white solid compounds at room temperature.
- Add together both solids to water separately to see a difference. No you lot cannot see a change. Both compounds requite colourless solutions. So what to do next?
- Add aqueous argent nitrate to colourless solutions. In one flask, a white precipitate is formed.
- Consider existing anions and cations of two solutions.
- In Sodium bromide solution, Na+, Br-, Ag+, NO3-
- In sodium nitrite, Na+, NOii-, Ag+, NO3-
When Ag+ and Br- ions are in the solution, it give AgBr white precipitate.
How to examination chloride ion in presence of bromide ion?
We can do concentrated sulfuric acrid and manganeese dioxide to examination chloride ion in the presence of bromide ion. Here how information technology does.
Manganeese dioxide - MnO2
Add together concentrated sulfuric acrid and heat the mixture. You tin come across a vapour of Brtwo in red brown colour. Then again add concentrated sulfuric acid and MnO2. A yello green Clii gas emits.
What are the coloured solutions when add concentrated excess aqueous HCl to transition metal ions?
When we add full-bodied excess aqueous HCl to transition metallic ions, complexes or coordination compounds are formed. Some 3d metal ions give coloured solutions with concentrated excess aqueous Cl- ions.
3d metal ion complexes when add concentrated excess aqueous Cl- ions
- [FeCl4]2- (aq) : yellowish
- [CoClfour]2- (aq) : blue
- [NiCl4]2- (aq) : blue
- [NiCl4]ii- (ethanol) : yellow dark-brown
- [CuCl4]two- (aq) : xanthous
How bromine and iodine are prepared past chlorine gas?
Chlorine is located nether iodine and bromine in the electrochemistry series. Therefore reducing of chlorine(Clii) to chloride(Cl-) is easier than Brtwo to Br- and Iii to I-. Bromine is obtained past the oxidation of Br- with chlorine gas in saline water. Iodine is similarly produced by passing chlorine gas through saline water containing I- ions.
Clii + 2I- → I2 + 2Cl-
Cl2 + 2Br- → Brtwo + 2Cl-
sodium bromide with copper presence of sulphuric acid
If you desire to release bromine gas, you have to add together concentrated sulfuric acid. If you use concentrated sulfuric acid in the presence of copper, copper is oxidized while sulfuric acid is reduced to sulfur dioxide considering concentrated sulfuric acrid is an oxidizing acrid.
How to identify metal halides with potassium ions
All potassium halides ( KF, KCl, KBr, KI ) are soluble in h2o and give colourless solutions.
- KF - white crystals, soluble in water and HF, but not soluble in booze.
- KCl - White crystals, soluble in water, not souble in ethanol.
- KBr - Colorless crystals or white granules or powder, soluble in h2o, Sparingly soluble in ethanol.
- KI - white solid, soluble in h2o, Slightly soluble in ethanol.
Only KI is soluble in HF. And KBr and KI are sparingly soluble in ethanol.
Which halide ion, chloride, bromide and iodide is more easy to oxidize?
Iodide ion is easily oxidize to Iii than bromide to bromine and chloride to chlorine.
Source: https://www.chemistryscl.com/advancedlevel/inorganic/qualitative_analysis/identify-halides/main.html
Post a Comment for "Elements of the Halogen Family __________ One Electron to Become Halide Ions."